Crediting Traditional Indigenous Foods in the CACFP
November 21, 2023
Child Nutrition Programs (CNP), including the Child and Adult Care Food Program (CACFP), strive to be inclusive of and adaptive to all cultures. An important aspect of this is making sure that culturally appropriates foods are being served. Indigenous groups eat certain foods that are not commonly consumed by other cultures, and those foods were not previously included in the Food Buying Guide (FBG) and were difficult to credit in CNPs.
In response, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has included traditional foods in the FBG. Not only does this list make program participation easier for indigenous groups, but it is also a great resource for any programs that serve indigenous groups.
Below are examples of traditional Indigenous Foods and how they credit in the CACFP according to the Food Buying Guide.
For more guidance please refer to the FBG and recent Technical Assistance memo about serving and crediting Indigenous Foods in the CACFP.
And for quick reference, download our guide that contains the crediting information for all 18 foods mentioned below.
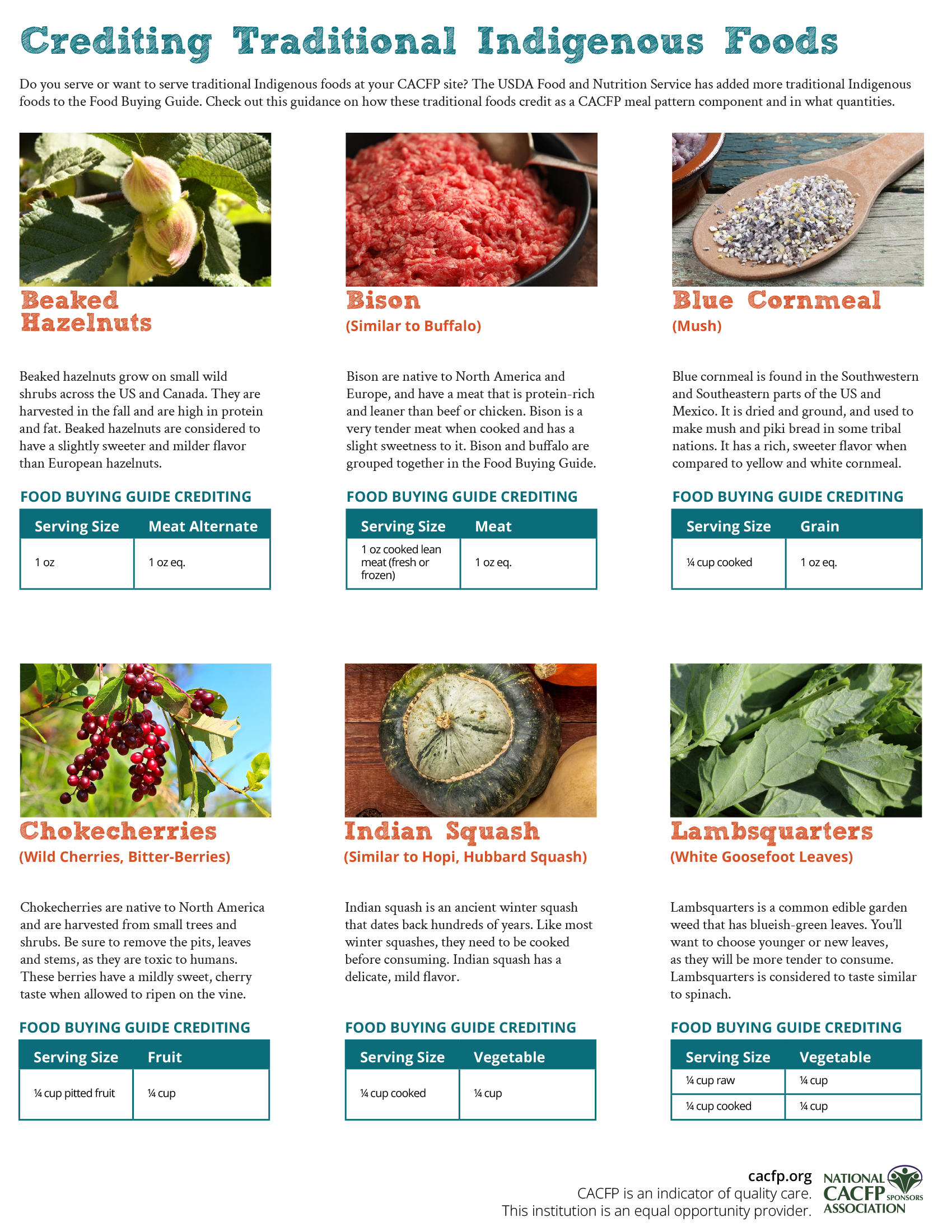
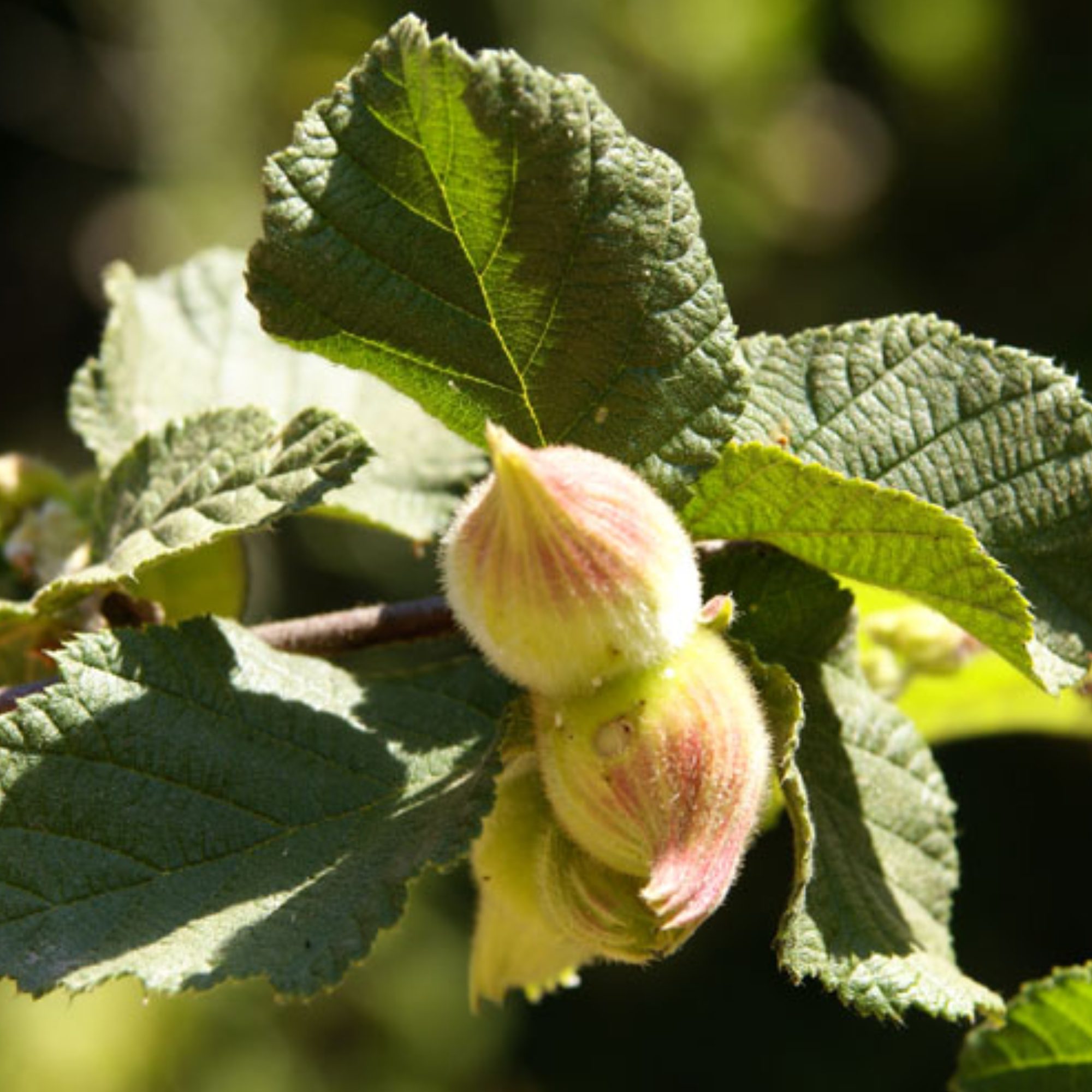
Beaked Hazelnuts

What is it?
The beaked hazelnut is considered a nut that grows on small wild shrubs across the United States and Canada. Harvested during the fall, these nuts are high in protein and fat. Typically, they are smaller than the European hazelnuts seen in grocery stores.
Taste
They are considered to have a slightly sweeter and milder flavor than the European hazelnuts.
Recipe Ideas
Try roasting the hazelnuts then crush them to sprinkle over oatmeal or blend them down to make hazelnut butter.
How to Credit
| Beaked Hazelnuts | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| 1 oz | 1 oz eq. |
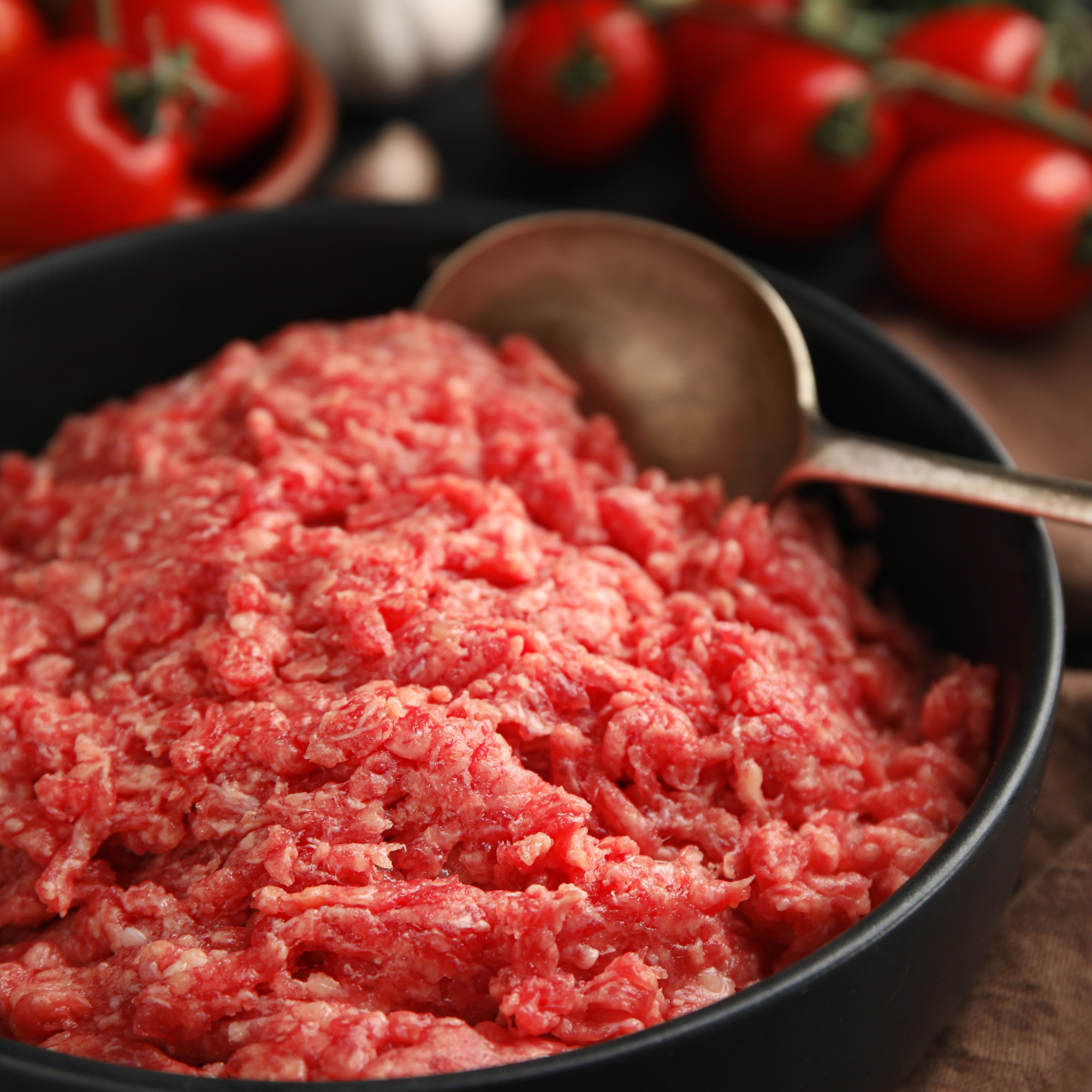
Bison

What is it?
Native to North America and Europe, bison are used for their meat that is protein-rich and leaner when compared to beef or chicken. When looking bison up in the Food Buying Guide, buffalo and bison are grouped together and indicated to have similar yields when cooked.
Taste
Very similar to the taste of beef, bison has a slight sweetness to it. Bison is a very tender meat when cooked.
Recipe Ideas
State (Montana) Child Nutrition Agency developed this recipe, Bison and Barley Soup, featuring local bison and fresh vegetables that are simmered in a tomato-based sauce.
How to Credit
| Bison (Similar to Buffalo) | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| 1 oz cooked lean meat (fresh or frozen) | 1 oz eq. |
Blue Cornmeal (Mush)
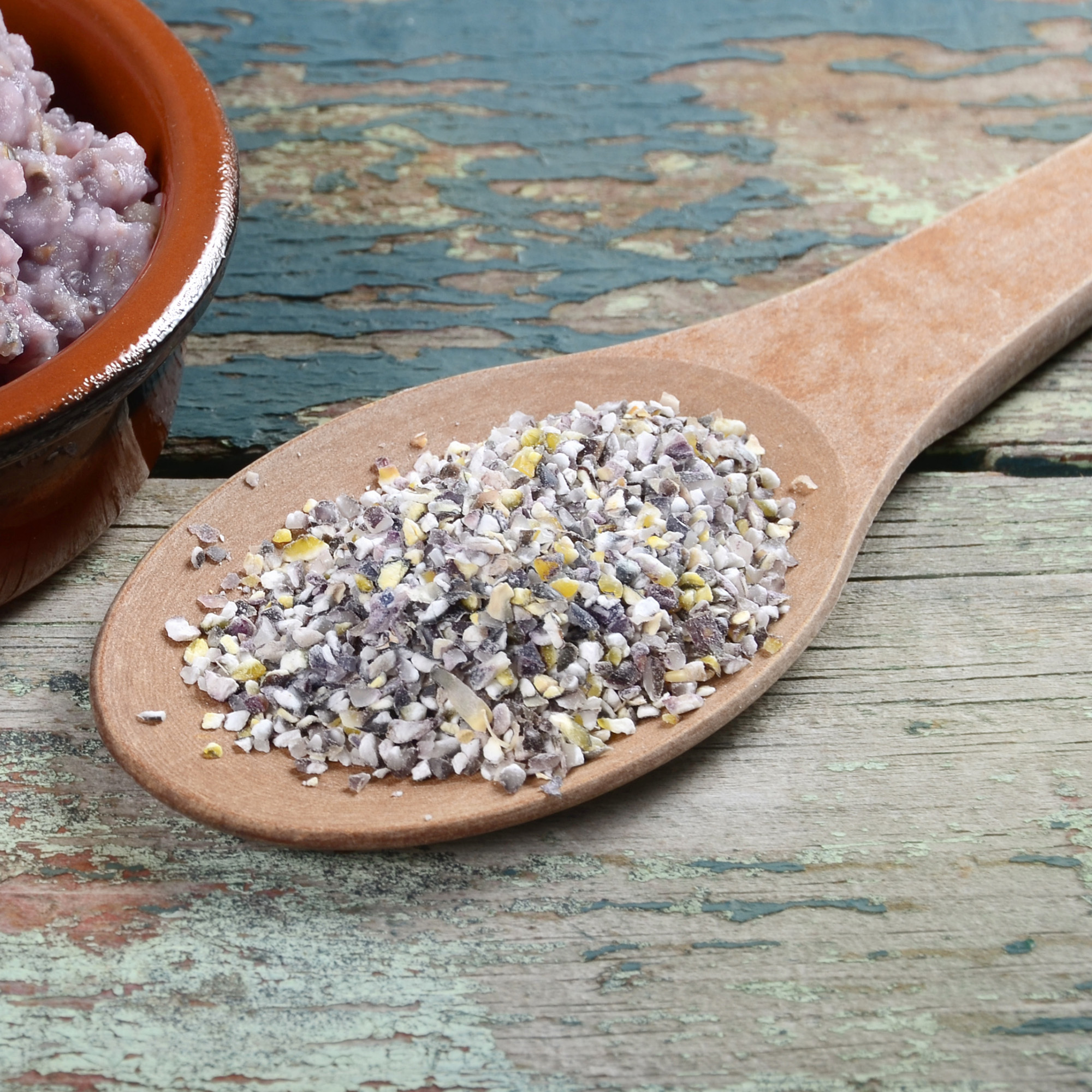

What is it?
Found in the southwestern and southeastern parts of the United States and in Mexico, this blue corn is dried and ground, and used to make mush and piki bread in some tribal nations. Commercially, blue corn is used for tortilla chips, cornbread and pancake mix.
Taste
Blue cornmeal has a rich, sweeter flavor in comparison to yellow and white cornmeal.
Recipe Ideas
Substitute the yellow cornmeal for the blue cornmeal to make Corn Pudding. Traditionally, you can use blue cornmeal to prepare mush, a porridge-like dish.
How to Credit
| Blue Cornmeal | Grain |
| ¼ cup cooked | 1 oz eq. |
Chokecherries (Wild Cherries, Bitter-Berries)
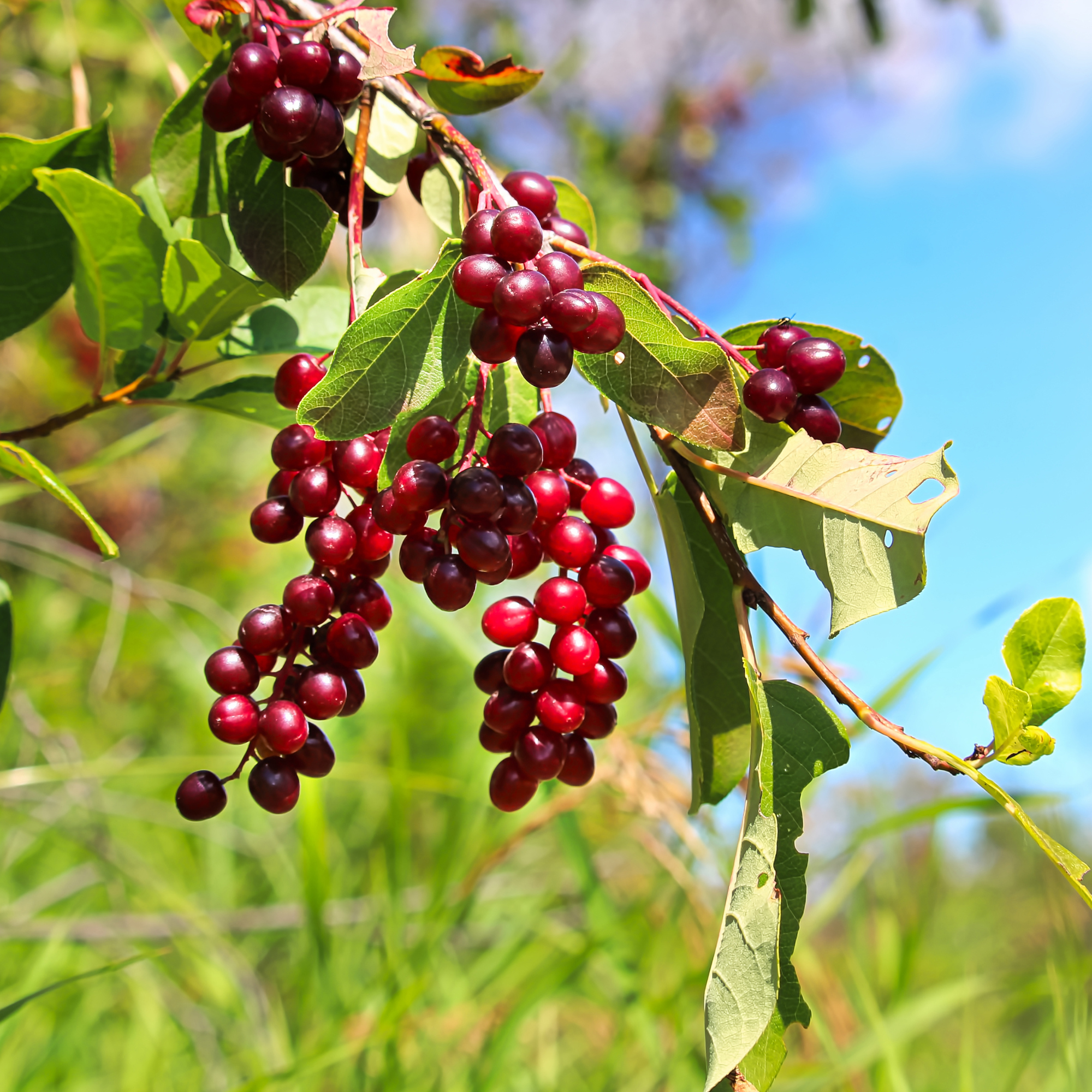

What is it?
Native to North American, chokecherries are wild harvested from small trees or shrubs. Be sure to remove the pits from the cherries before serving with these! It’s important to note that if you are harvesting this fruit, that you remove the leaves, stems and seeds from the plant as they are toxic to humans. There are variations of chokecherries based on the region they grow. You may have Eastern, Western or black chokecherries in your area.
Taste
If chokecherries are harvested too early, you will find they taste bitter and sour. Allowing chokecherries to ripen on the vine prior to picking will give you a mildly sweet, cherry taste.
Recipe Ideas
Replace the berries you add into muffins or pancakes with chokecherries. Add into a fruit salad.
How to Credit
| Chokecherries | Fruit |
| ¼ cup pitted fruit | ¼ cup |
Indian Squash (Similar to Hopi, Hubbard Squash)
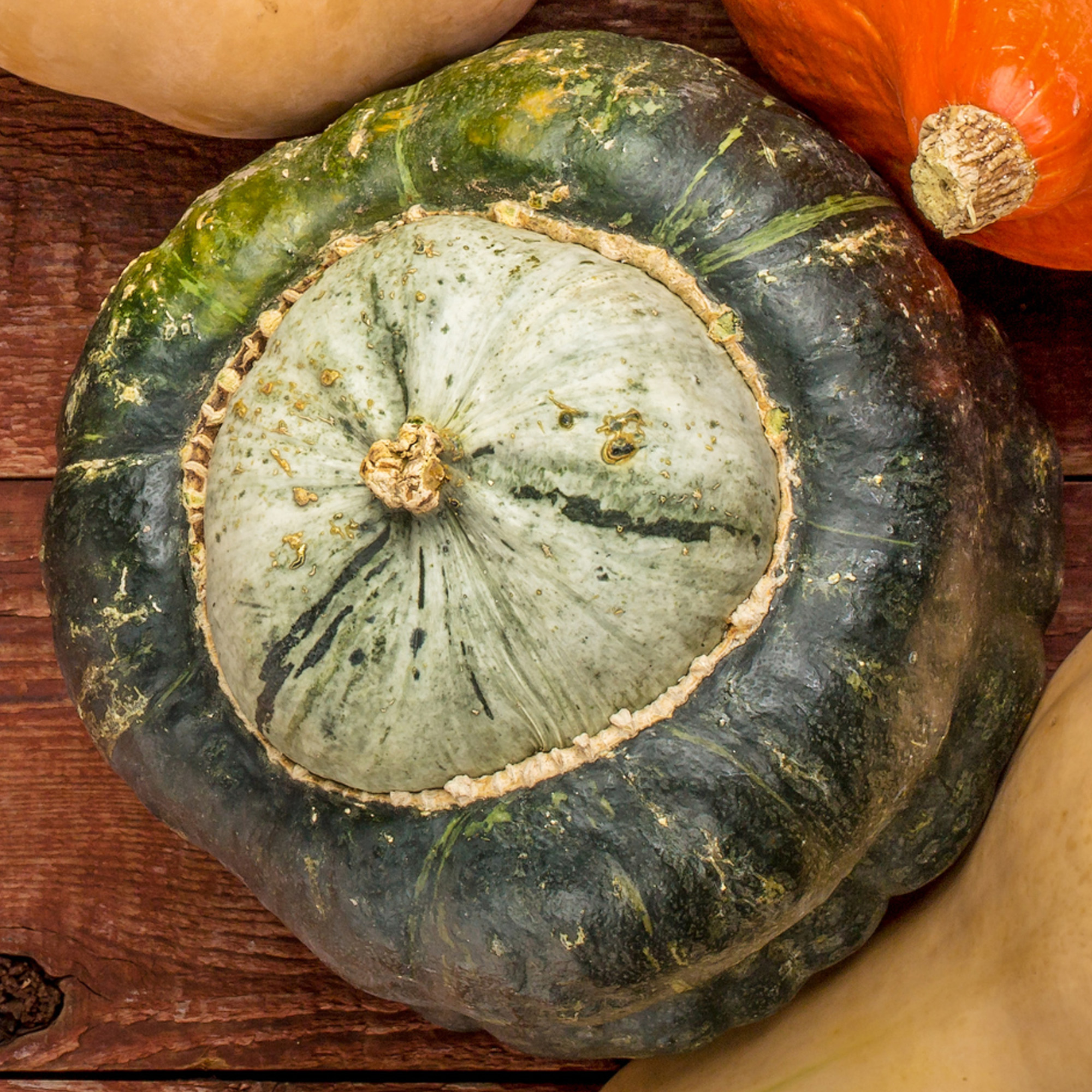

What is it?
Indian squash is an ancient winter squash that dates back hundreds of years. Like most winter squashes, these need to be cooked before consuming.
Taste
It is described as having a delicate mild flavor.
Recipe Ideas
Try substituting butternut squash with this Indian squash in the recipe, Stir-Fry Fajita Chicken, Squash and Corn.
How to Credit
| Indian Squash | Vegetable |
| ¼ cup cooked | ¼ cup |
Lambsquarters (White Goosefoot Leaves)
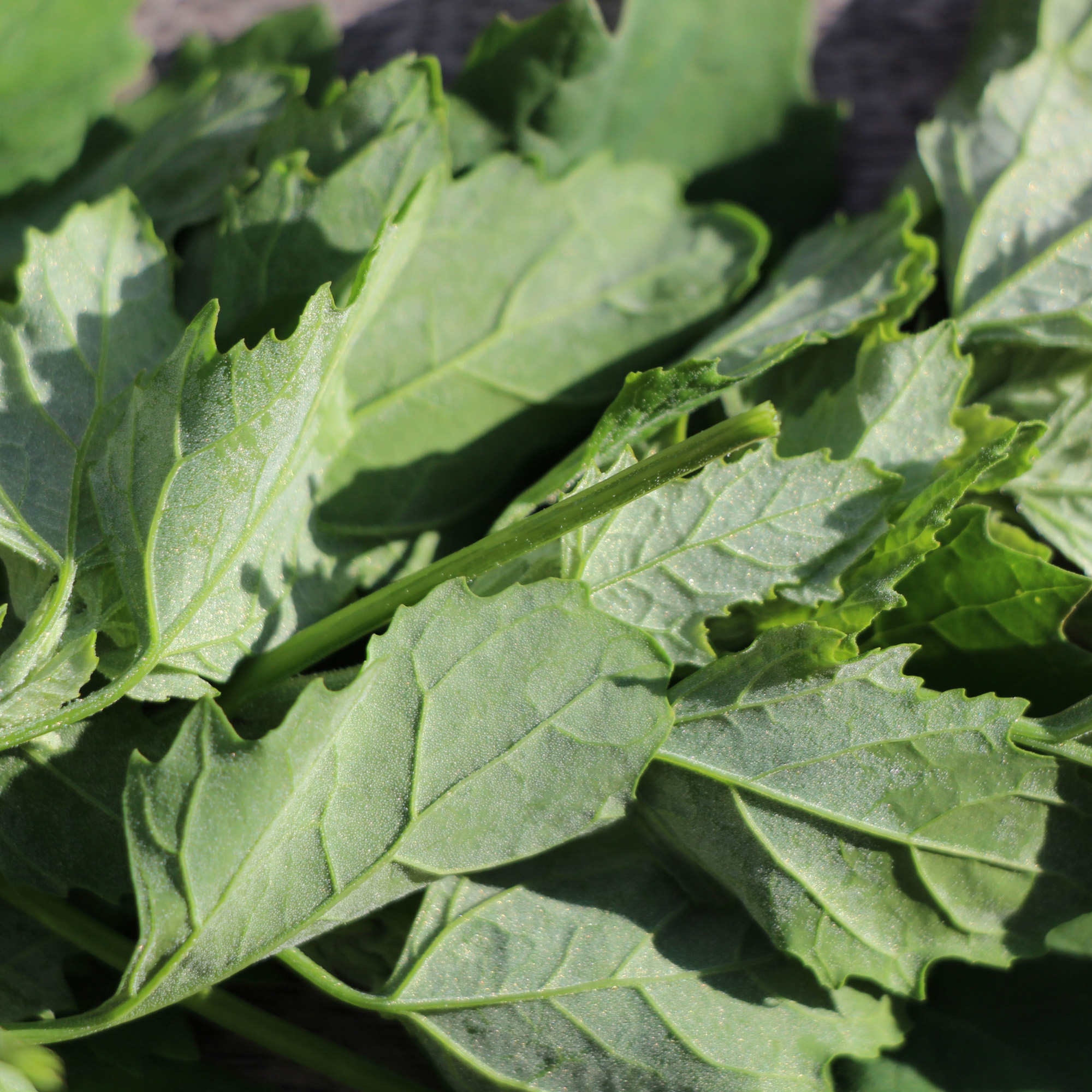

What is it?
This common edible garden weed that has bluish-green leaves and stems are tender when young. Can be harvested and used in nutritious dishes.
Taste
You’ll want to choose younger or new leaves as they will be more tender to consume. Considered to taste similarly to spinach.
Recipe Ideas
Try steaming, sauteing or adding it into your favorite soup.
How to Credit
| Lambsquarters | Vegetable |
| ½ cup raw | ¼ cup |
| ¼ cup cooked | ¼ cup |
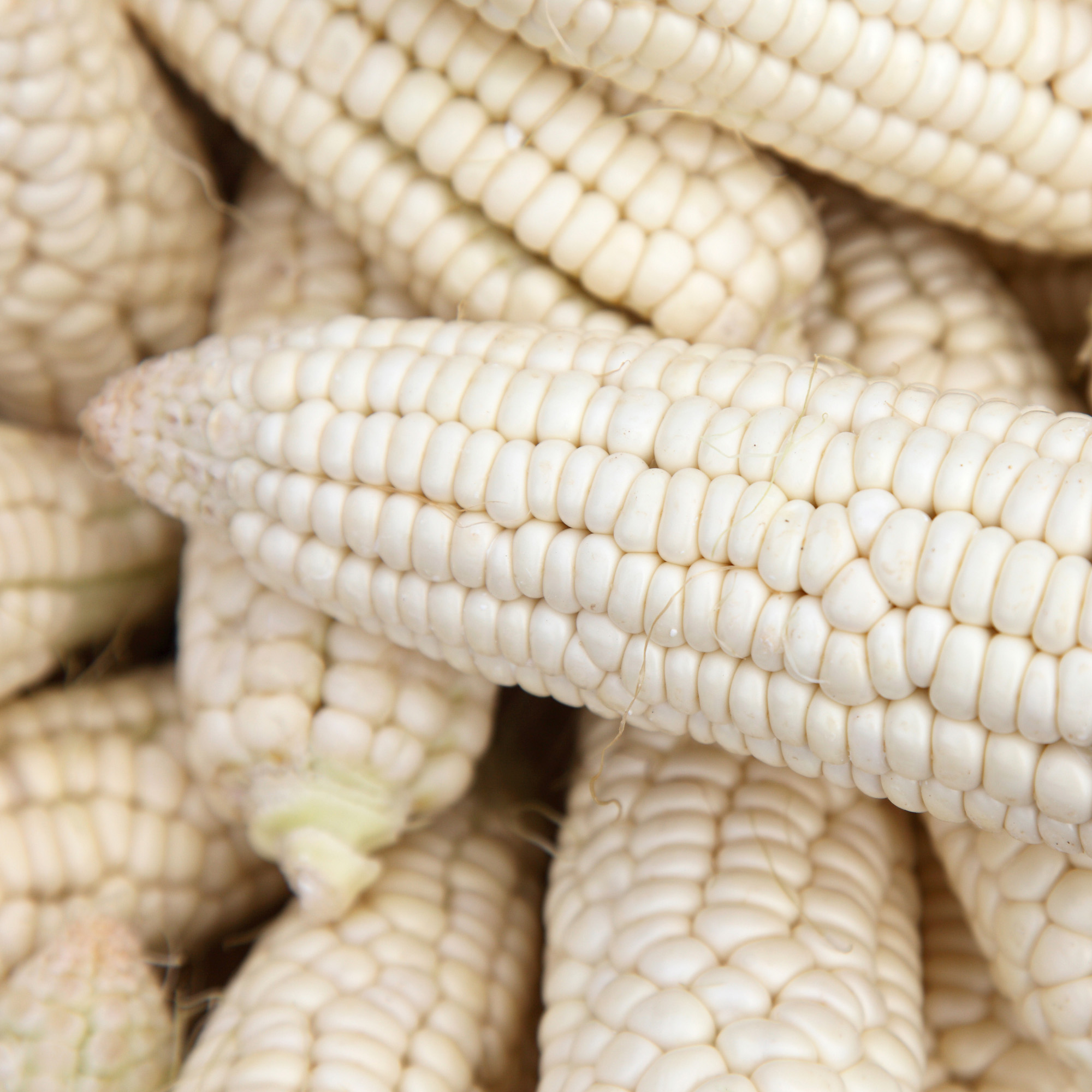
Native White Corn (Not Ground)

What is it?
This type of sweet corn has white kernels and can be eaten right off the cob or cooked into your favorite dish.
Taste
When ripe, they are sweet, tender, and have a delicate flavor that can be prepared fresh or cooked such as roasting steaming, boiling, and grilling.
Recipe Ideas
Try adding this corn to the Corn, Zucchini, and Tomato Pie recipe.
How to Credit
| Native White Corn, Fresh | Vegetable |
| ¼ cup cooked ( ½ medium cob) | ¼ cup |
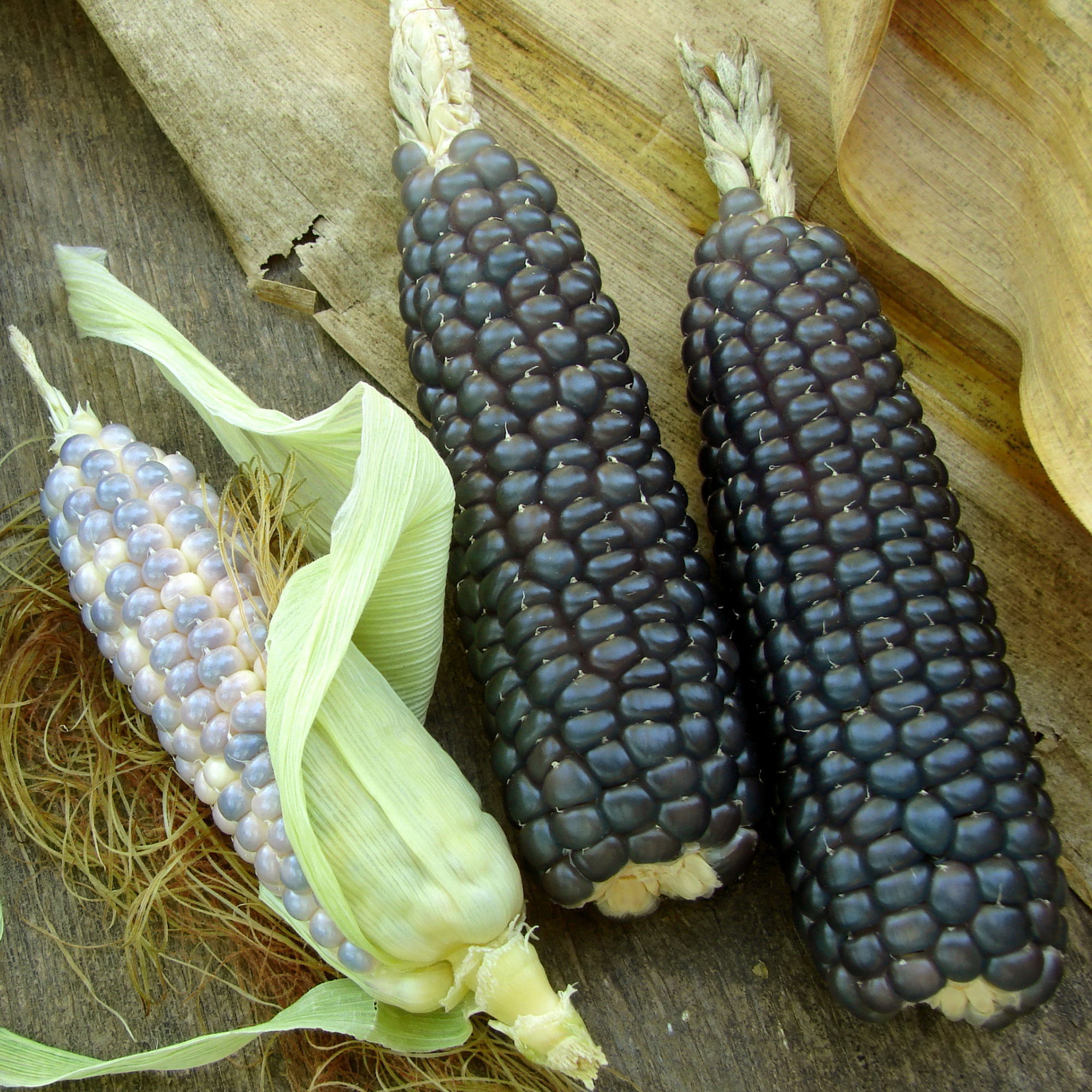
Native Whole Blue Corn Kernel (Not Ground)

What is it?
Similar to fresh sweet native white corn and yellow corn, this type of blue corn can be eaten on the cob or cooked as part of a meal or snack.
Taste
Like yellow sweet corn, when blue corn is cooked, it will showcase its natural sweet flavors.
Recipe Ideas
Make your dish more colorful by adding blue corn into salads, stews, casseroles and soups.
How to Credit
| Native Whole Blue Corn Kernel, Fresh (Not Ground) | Vegetable |
| ¼ cup cooked (½ medium cob) | ¼ cup |
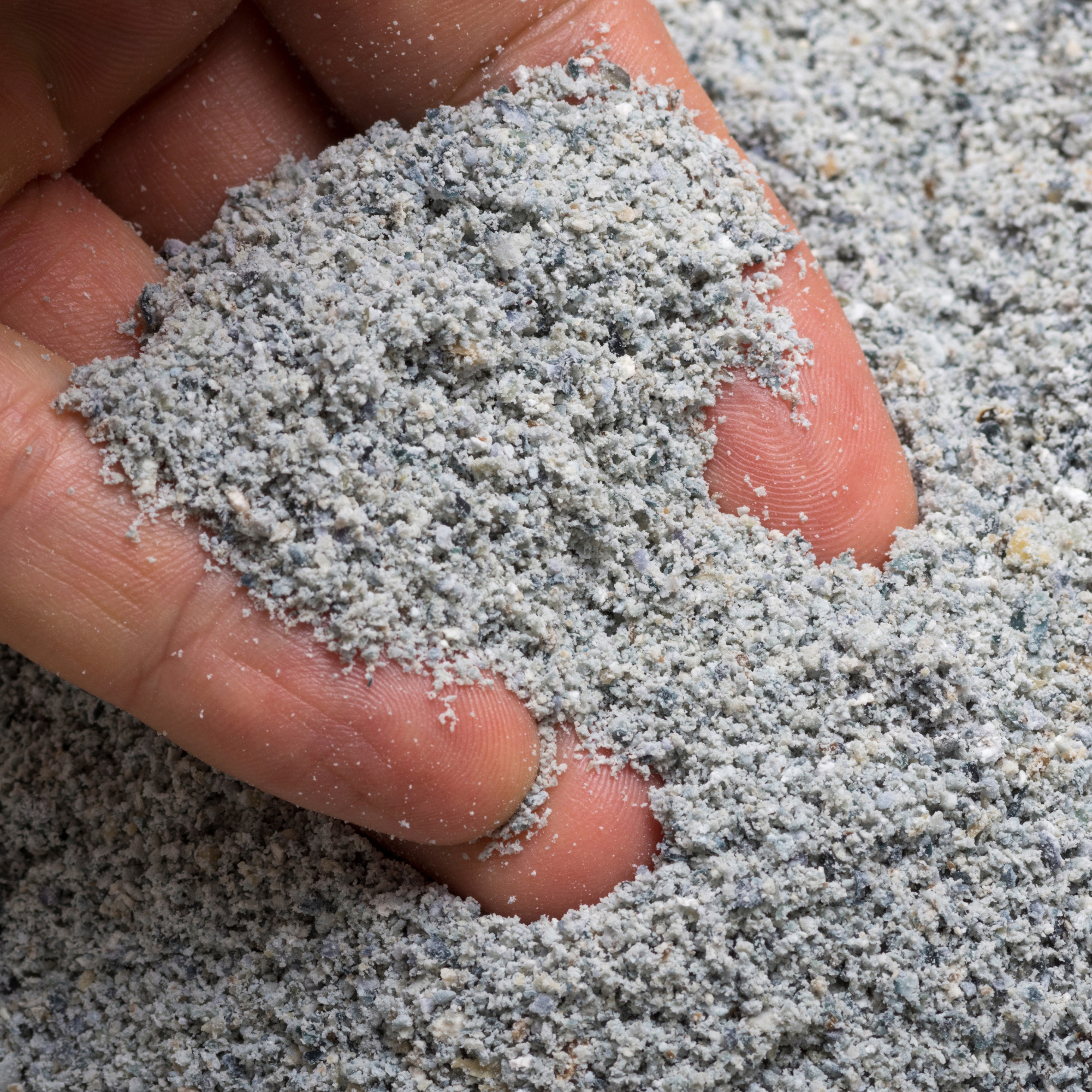
Native Whole Blue Corn Kernel (Ground into Flour)

What is it?
Blue corn is dried, sometimes roasted and then ground into flour.
Taste
This flour is described as having sweet, earthy, and nutty flavors.
Recipe Ideas
Can be prepared in many ways such as used in tamales, cornmeal pancakes, or cornbread like this recipe for Blue Cornbread Muffins.
How to Credit
| Native Whole Blue Corn Kernel, Fresh (Ground) | Grain |
| ¼ cup cooked | ½ oz eq. |
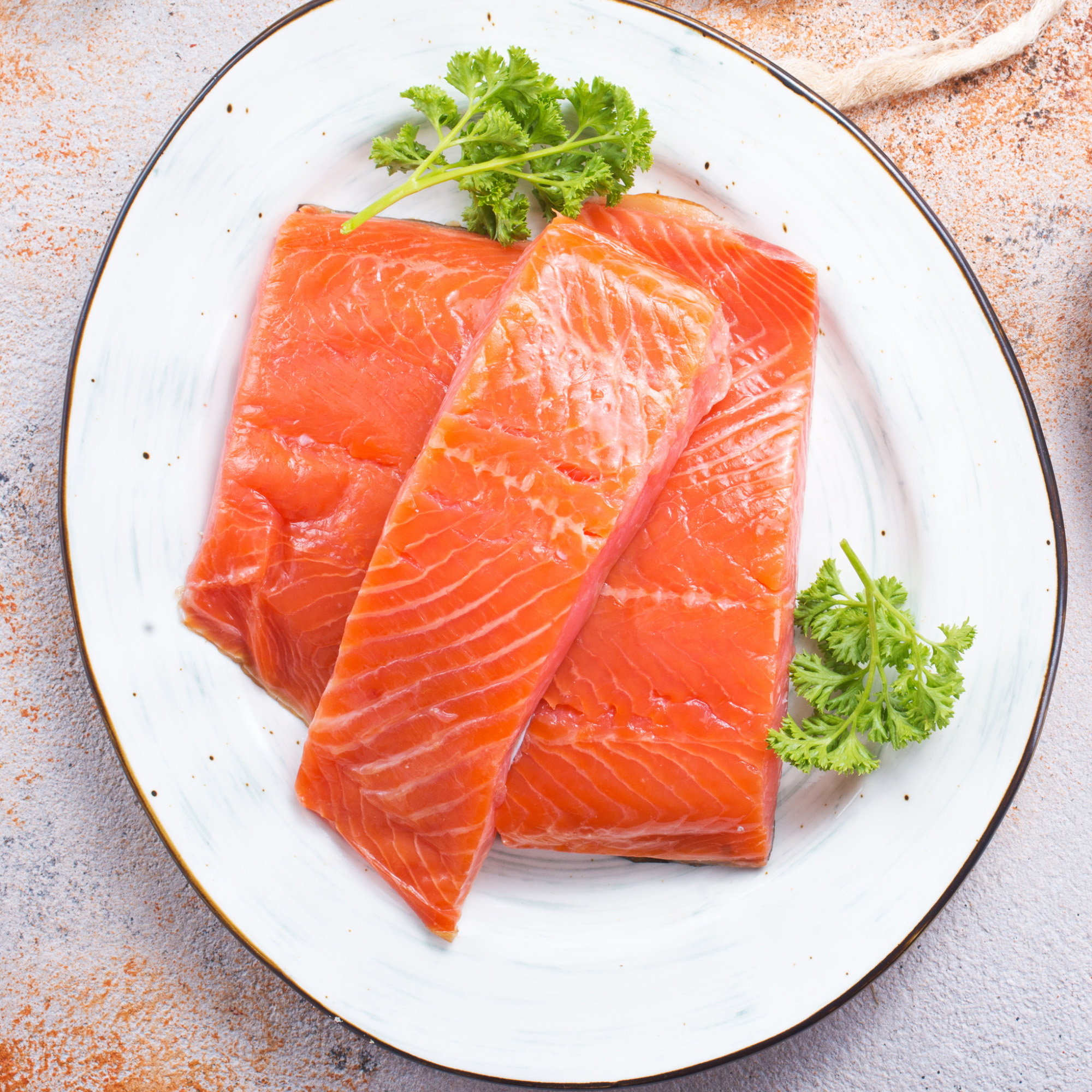
Red (Sockeye) Salmon

What is it?
This fish is found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and adjoining rivers. These naturally red colored salmon contains a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Taste
Red salmon is firmer in texture and has a more intense “salmony” flavor when compared to pink salmon.
Recipe Idea
Try using red salmon in a Salmon Corn Chowder recipe.
How to Credit
| Red (Sockeye) Salmon | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| 1 oz cooked fish (fresh or frozen) | 1 oz eq. |
| 1 oz pouch pack or canned, dried fish | 1 oz eq. |
Salmonberries (Similar to Raspberries, Wild Raspberries)
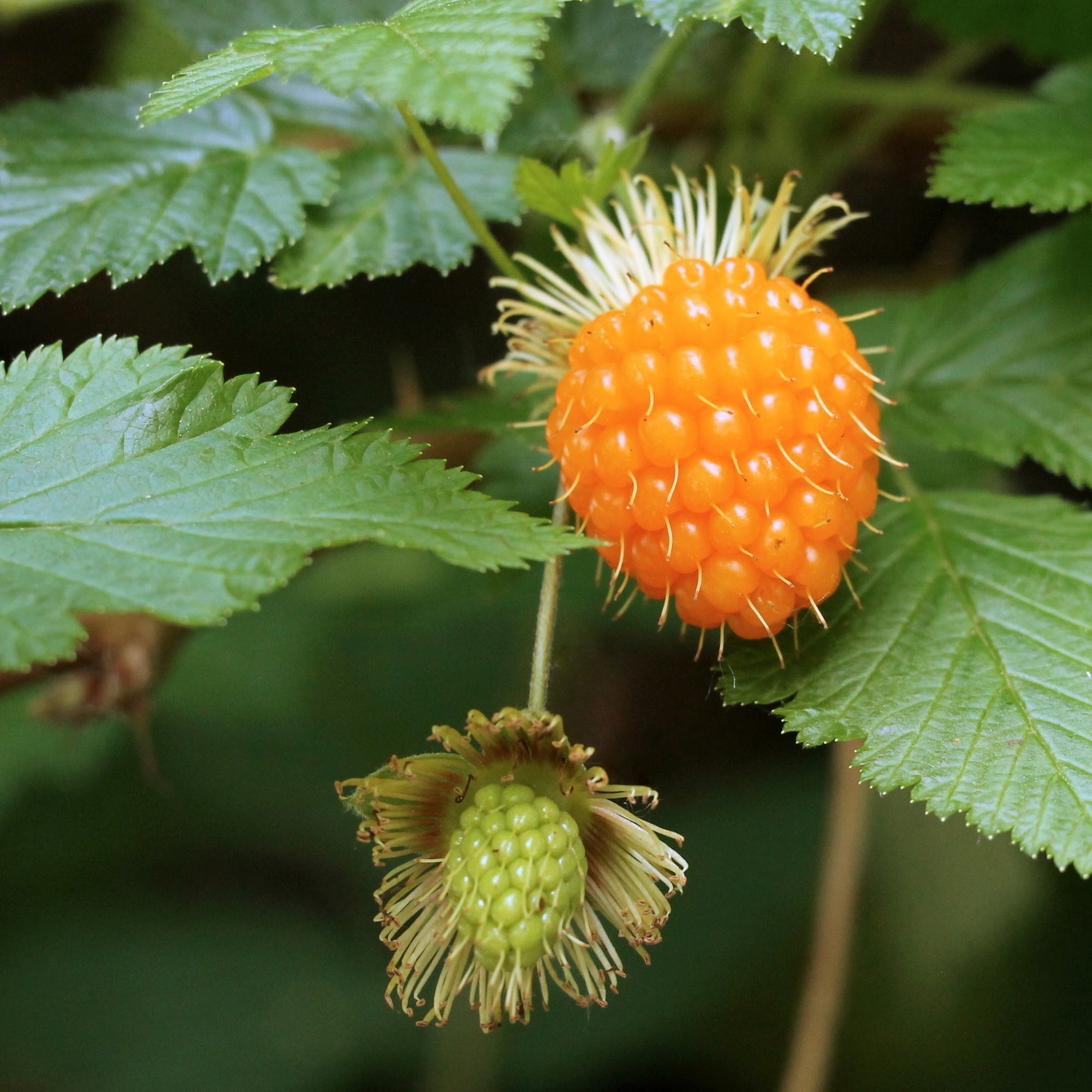

What is it?
Also known as thimbleberries or Alaskan berries, salmonberries are like raspberries or blackberries. You can typically find these berries in California, Alaska or Canada. Their color varies from yellow to orange and red.
Taste
If you compare salmonberries to raspberries, they have a more subtle flavor and are not as sweet. These berries are tart, similar to rhubarb.
Recipe Ideas
Usually, salmonberries are cooked down and mixed with sweeter fruit due to its tart flavor and are filled with many seeds. Try cooking salmonberries with strawberries and then add on top to yogurt or try baking it into a whole wheat muffin.
How to Credit
| Salmonberries (Similar to Raspberries and Wild Raspberries) | Fruit |
| ¼ cup raw, whole fruit | ¼ cup |
Tepary Beans (Similar to Navy Beans or Peas)
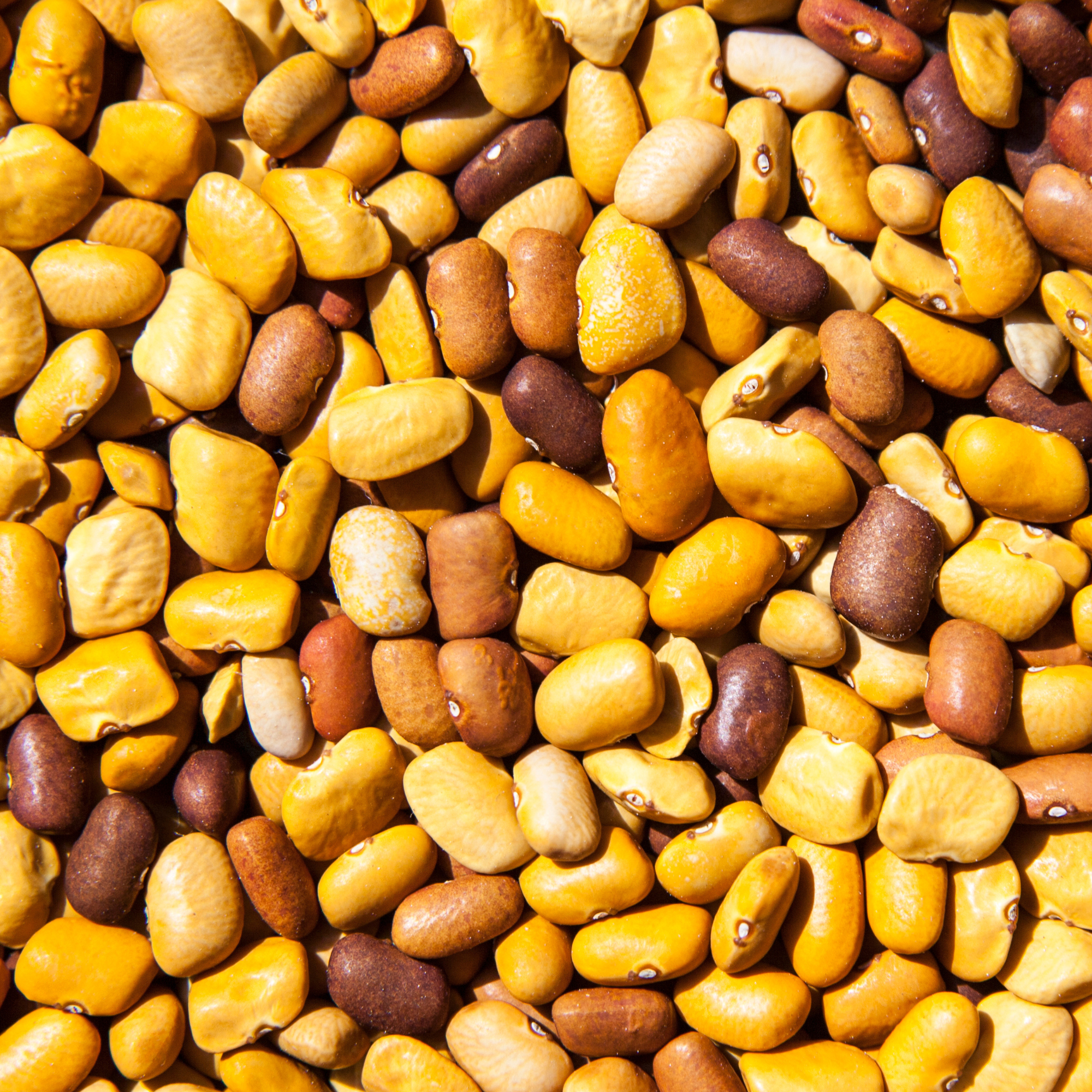

What is it?
These are native, annual legumes found in Arizona, New Mexico, Texas and Mexico. They love to grow in dry regions around the world. These legumes come in a variety of black, brown, and white tepary beans.
Taste
They have a creamy texture and vary in flavor depending on the bean color. The brown bean can give a nutty, earthy flavor while the white beans can give a sweeter flavor.
Recipe Ideas
Try adding cooked tepary beans in soups, stews, salads or even on their own as a side dish.
How to Credit
| Tepary Beans (Similar to Navy Beans or Peas | Vegetable | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| ¼ cup cooked | ¼ cup | 1 oz eq. |
Whole Cuts Sheep
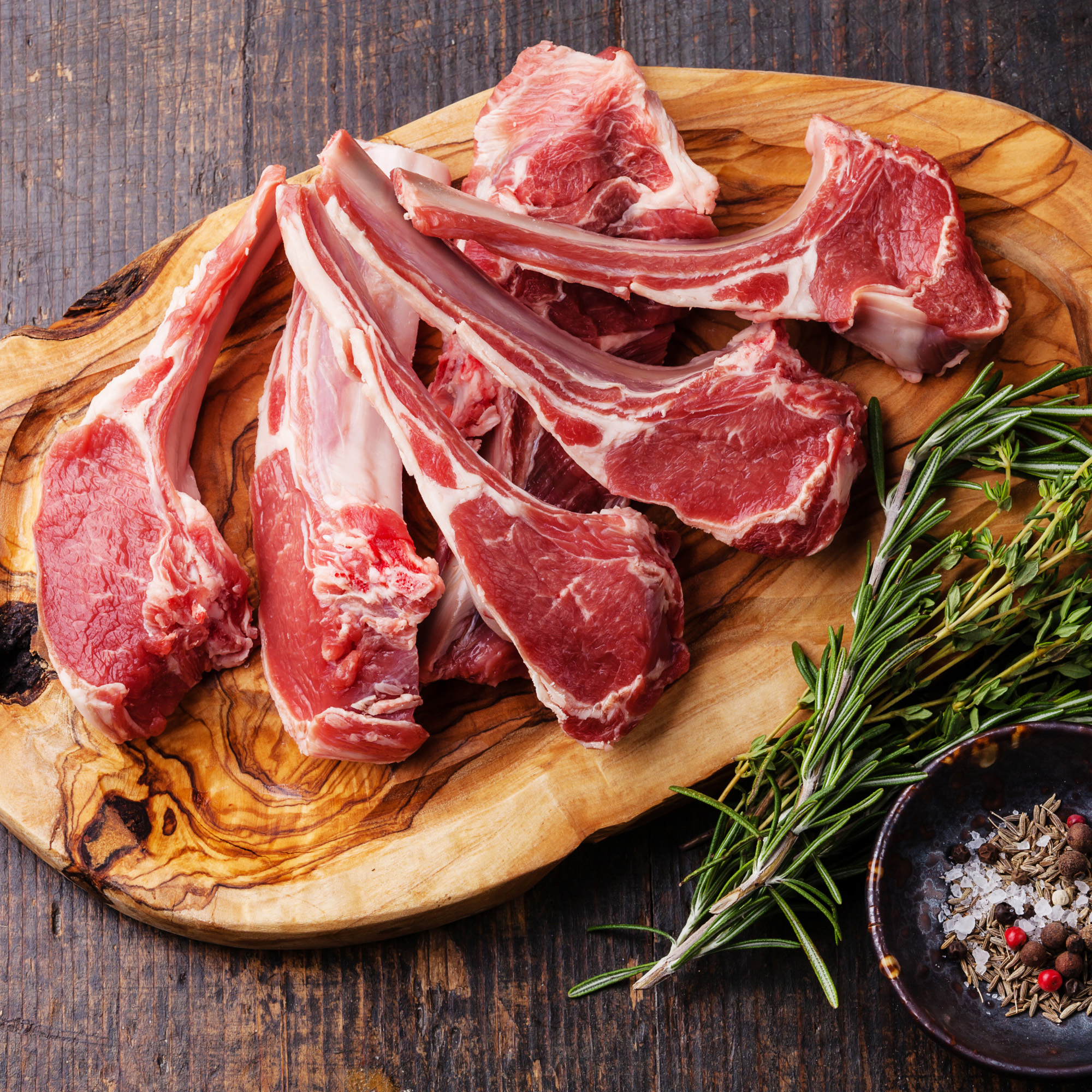

What is it?
Depending on the age of the sheep, it can be labelled differently. Lamb meat are sheep younger than 1 and mutton meat are older sheep.
Taste
Sheep has a gamey flavor, however lamb will have a milder flavor.
Recipe Ideas
When cooking with lamb, you can grill, braise or roast. For mutton, use slow cooking methods to help tenderize the meat.
How to Credit
| Whole Cuts Sheep (Similar to Lamb) | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| 1 oz cooked lean meat (fresh or frozen) | 1 oz eq. |
Whole Cuts Venison (Elk or Deer)
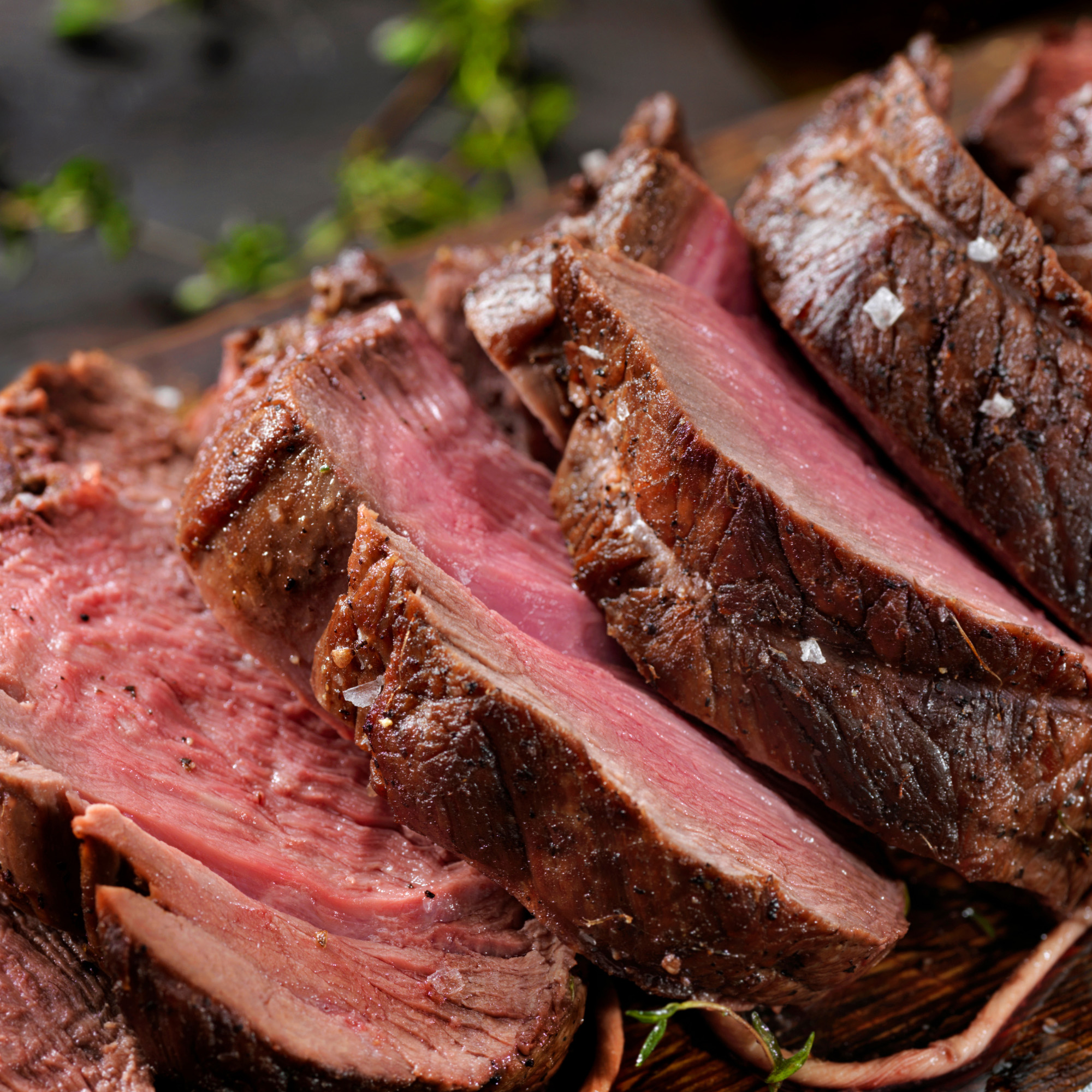

What is it?
Venison is a lean meat from native deer or elk. Used in place of other types of red meat in recipes.
Taste
Venison tastes somewhat like beef but has a richer and earthy taste.
Recipe Ideas
Add venison into a stew, roast it, or marinate it before grilling.
How to Credit
| Whole Cuts Venison (Similar to Sitka, Elk) | Meat/Meat Alternate |
| 1 oz cooked lean meat (fresh or frozen) | 1 oz eq. |
Wild Plums
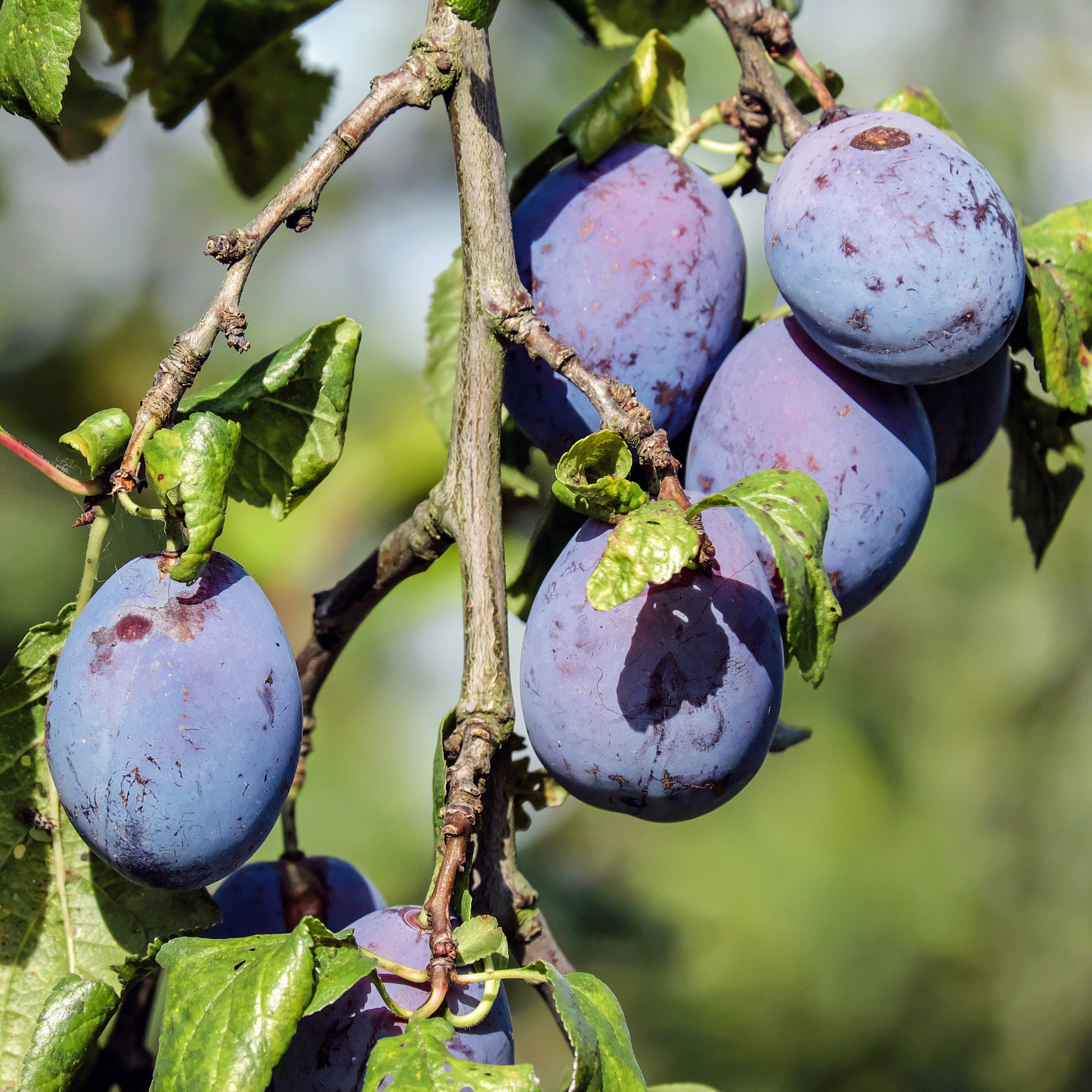

What is it?
Wild plums are grown on trees in North American and can come in different colors like red, yellow, and orange. Have been known to be part of some Tribal Nation diets or used to make red dye.
Taste
Depending on the wild plum, they can taste sour and sweet, sometimes bitter. If you find tart plums, it is best to cook them.
Recipe Ideas
For sweeter plums try it in Telly’s Tasty Plum Salsa or as a topping on oatmeal for breakfast.
How to Credit
| Wild Plums (Similar to Plums) | Fruit |
| ¼ cup quartered fruit | ¼ cup |
Wild Raspberries
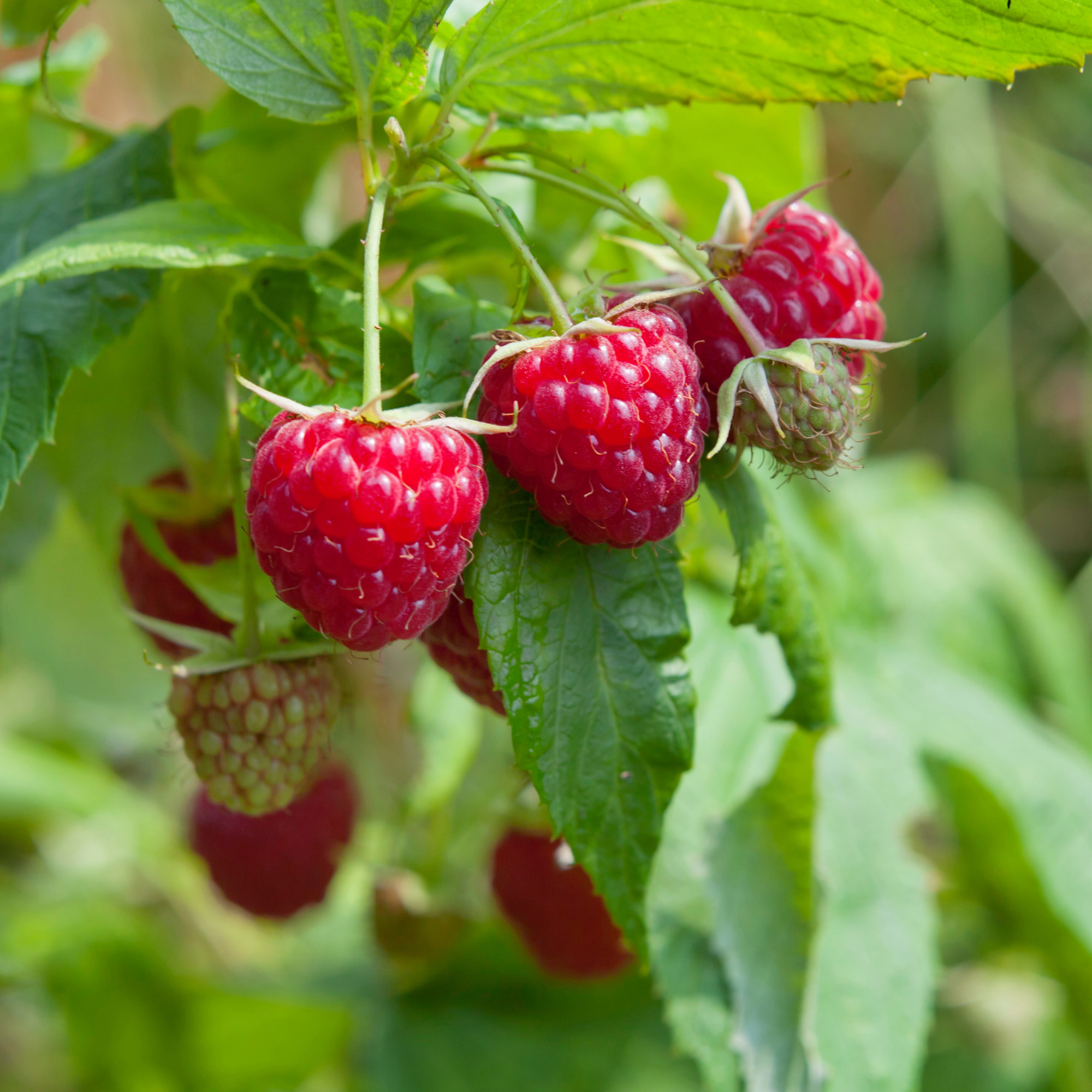

What is it?
Cultivated wild raspberries can be picked from bushes found throughout eastern North America. This fruit can appear in a variety of colors such as red, gold, and purple. Once harvested, this fruit does not continue to ripen so choose ones with darker or more vibrant colors.
Taste
Wild raspberries have a tart, juicy, and sweet taste.
Recipe Ideas
They can be eaten as is or added to a salad or smoothie.
How to Credit
| Wild Raspberries (Similar to Raspberries and Salmonberries) | Fruit |
| ¼ cup raw, whole fruit | ¼ cup |
Wild Rice
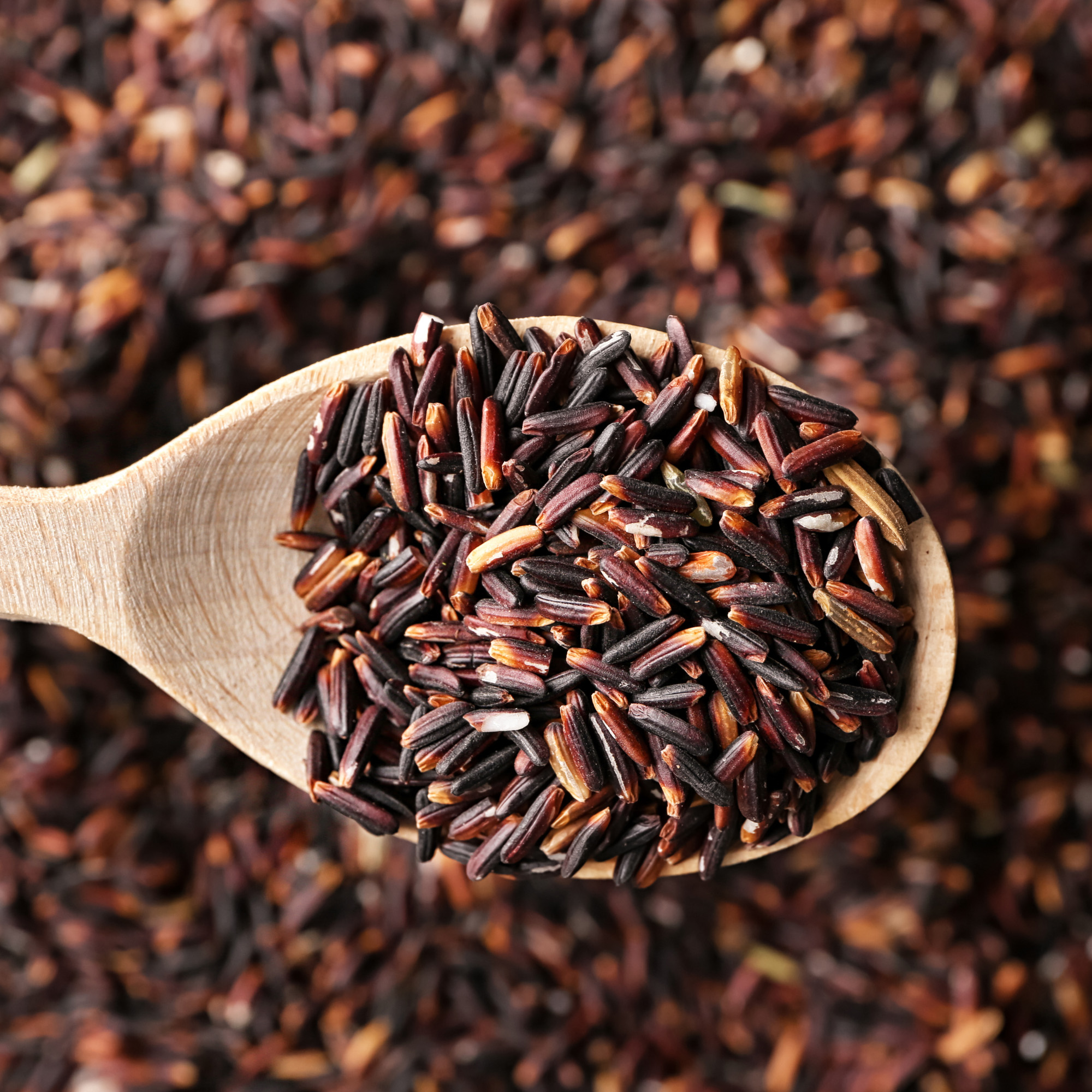

What is it?
Wild rice is an aquatic grass that naturally grows in the waterways in North America. Can be prepared like white or brown rice.
Taste
Wild rice has a nutty, earthy flavor.
Recipe Ideas
Try making wild rice stuffing, substitute brown rice for wild rice in dishes or try it in a Creamy Wild Rice recipe.
How to Credit
| Wild Rice | Grain |
| ¼ cup cooked | ½ oz eq |